This article will explore the need for overcurrent protection for current-carrying tap conductors. CE Code Rule 14-100 requires overcurrent protection where a conductor receives a supply of current and at each point where the size of conductor is decreased. The size of the overcurrent protection is to be not greater than the allowable ampacity of the conductor in accordance with Rule 14-104. In addition, Subrule (2) of Rule 14-104 mandates the maximum size of overcurrent protection for conductor sizes No. 14 to 10 AWG as:
- 15 A for No. 14 AWG copper conductors
- 20 A for No. 12 AWG copper conductors
- 30 A for No. 10 AWG copper conductors
- 15 A for No. 12 AWG aluminum conductors
- 25 A for No. 10 AWG aluminum conductors
The provisions of Rule 14-104, however, do allow for three exceptions. The first exception permits 15 A overcurrent protection for tinsel cords, equipment wire, and flexible cord size Numbers 16, 18, and 20 AWG copper. The second exception recognises that overcurrent protection may not be available with the same value as the allowable ampacity of the conductor, and allows the use of Table 13 for correlation between specific rating/setting of overcurrent device an allowable ampacity of conductors smaller than the overcurrent device rating or setting for applications with a maximum value of 600 A. The third exception is for conductors supplying specific equipment like capacitors, separate cooking units, motors and heaters that are covered by other rules in the CE Code. These installation executions will be discussed later in this article.
Back to Rule 14-100
Rule 14-100 gives seven exceptions where overcurrent protection can be omitted. The first exception detailed in Item (a) does not require overcurrent protection for a smaller conductor or where a conductor receives a current supply where the overcurrent protection installed upstream of the tap adequately protects the smaller conductor. An example of this is where the smaller conductor is connected to a conductor where the size has been increased to meet the voltage drop requirements of Rule 8-102 (1).
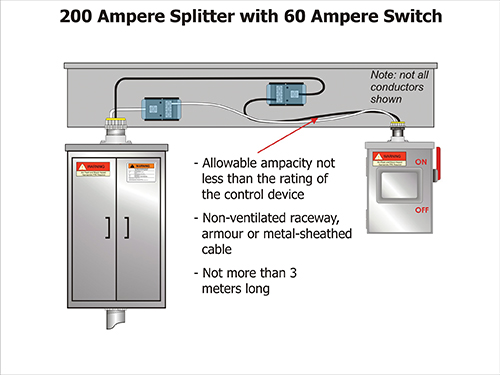
Items (b) to (g) of Rule 14-100 recognises that it is not always possible to provide overcurrent protection where a conductor receives a supply of current. This allows the installation of a smaller tap conductor. Item (b), also known as the “3M Rule”, allows a smaller conductor with an allowable ampacity not less than the rating of the control device being supplied provided the smaller conductor where installation between enclosures is in an armoured cable, metal-sheathed cable or in non-ventilated raceways, and the total length of the smaller conductor is limited to not more than 3m in length (illustrated in figure 1).
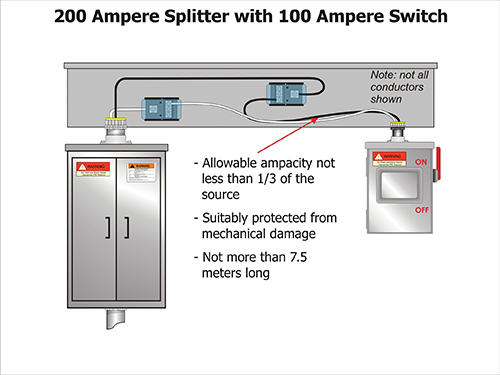
Item (c), also known as the “one-third rule”, allows a smaller conductor not exceeding 7.5 m with an allowable ampacity not less than one-third that of the conductor being tapped from, provided the smaller conductor terminates at a single overcurrent device and is protected from mechanical damage (illustrated in figure 2).
Item (d) allows a conductor provided with mechanical protection supplied from a high voltage transformer that terminates in a single overcurrent device rated not greater than the conductor allowable ampacity provided that the high voltage primary overcurrent protection is a fuse rated not more than 150% or the primary full load ampacity, or a breaker rated not more that 300% of the primary full load ampacity in accordance with Rule 26-252.
Item (e) allows a control circuit conductor not smaller than No. 14 AWG with an overcurrent device rated not more than 300% of the allowable ampacity of the control circuit conductor provided that the opening of the control circuit would not create a hazard.
Item (f) allows a smaller conductor with an allowable ampacity not less than one-third of the conductor being tapped that supplies a transformer with a secondary conductor that terminates in a single overcurrent device rated not less than the secondary conductor allowable ampacity where the total length of one of the primary and secondary conductors does not exceed 7.5 m. In this case, both the primary and secondary conductors will need protection from mechanical damage.
Item (g) recognises (the smaller) low voltage overhead or underground conductors provided that where the conductor enters a building, the conductors are installed as a consumer service conductor and terminates in service equipment.



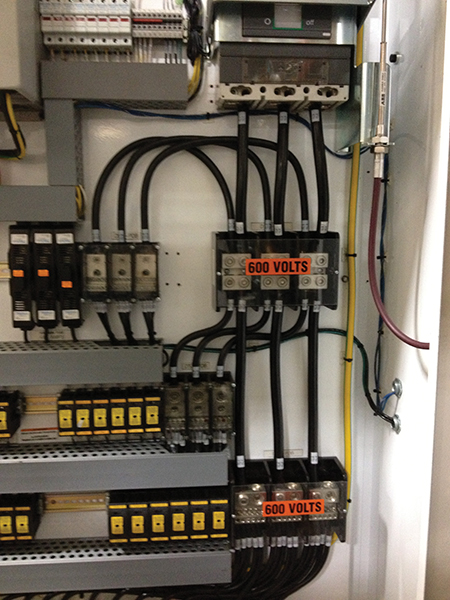
See photo 4 for an example of an installation that is not in compliance with CE Code Rule 14-100; notice the tap conductors connected to tap conductors.
Exceptions to Rules 14-100 and 14-104
Rule 26-208 allows a smaller tap conductor to supply a single capacitor provided the tap is supplied from a branch circuit that supplies two or more capacitors, the tap is not longer than 7.5 m, has an allowable ampacity not less than 135% of the rated current of the capacitor, and the tap has an allowable ampacity within one-third that of the branch circuit conductors.
Similar to Rule 26-208, Rule 26-246 allows a smaller tap conductor fed from a branch circuit to supply an individual built-in cooking unit provided the tap length does not exceed 7.5 m, has an allowable ampacity not less than the individual built-in cooking unit, and the tap has an allowable ampacity within one-third that of the branch circuit conductors.
Rules 28-106 and 28-108 allow the overcurrent protection to be set at more than the allowable ampacity of the conductor where the conductor is sized not less than 125% of a single motor full load current rating, and conductors used to supply a group of motors sized at not less than 125% of the largest motor full load current rating plus 100% of the motor full-load current of the remaining motor in the group. In accordance with Table 29 of the CE Code, the setting of the overcurrent protection could be as high as 400% (where the 300% overcurrent device will not allow the motor to start) of the motor full load rating when installed in accordance with Rule 28-200. For a group of motors utilising group installation motor controllers, the overcurrent protection ahead of the group installation motor controllers can be set at the lesser of the maximum rating marked on the motor controller or the calculated maximum overcurrent protection for the group of motors in accordance with Rule 28-204 for a feeder and Rule 28-206 for a branch circuit. The size of these tap conductors is required to have an allowable ampacity not less than one-third that of the setting of the overcurrent device ahead of the group of motors, and the length of the conductor from the overcurrent device ahead of the group of motors to the motors cannot exceed 7.5 m.
Rule 30-412 allows a 20 A overcurrent protection for a No.14 AWG copper conductor used to supply a single luminaire and luminaires marked as suitable for continuous row mounting provided the length of the No. 14 AWG conductor does not exceed 7.5 m and the ampere rating of the single luminaire or the luminaires mounted in a continuous row does not exceed the allowable ampacity of the No. 14 copper conductor.
Rule 62-114 allows an overcurrent protection set at not more that 300% of the allowable ampacity of a branch circuit conductor used to supply two or more heating fixtures, heating cable sets, heating panel sets, or parallel heating sets are grouped on a single branch circuit, the non-heating leads of heating cable sets, heating fixtures, and taps to heating cable sets, heating fixtures, and strip systems provided the length of the branch circuit tap conductor does not exceed 7.5 m.













Find Us on Socials