Emergency preparedness is crucial for individuals, communities, and organizations to effectively respond to and mitigate the impact of various unforeseen events, such as natural disasters, power outages, and other emergencies. It involves planning, organizing, and implementing measures to minimize potential risks and ensure the safety and well-being of people, infrastructure, and essential services.
By Andrew Browne, P. Eng., Assistant Chief Engineer
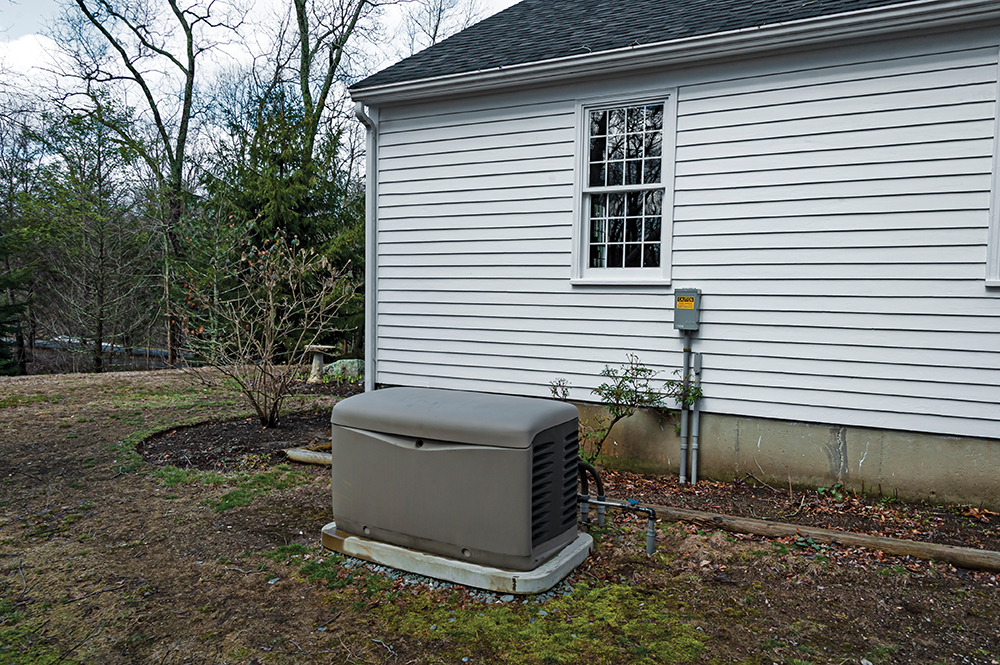
One essential aspect of emergency preparedness is the installation of backup power systems. These systems play a vital role in providing electricity during power outages. Generators are indispensable assets for various industries, emergency services, and residential applications, providing backup power during outages and powering critical systems. However, their operation entails inherent risks, including electrical hazards and potential malfunctions that could compromise safety and reliability. In this context, electrical inspectors play a crucial role in upholding generator safety standards and ensuring their reliable performance. This article explores the vital responsibilities of electrical inspectors and the significance of their contributions in promoting generator safety and reliability.
Conducting Thorough Inspections
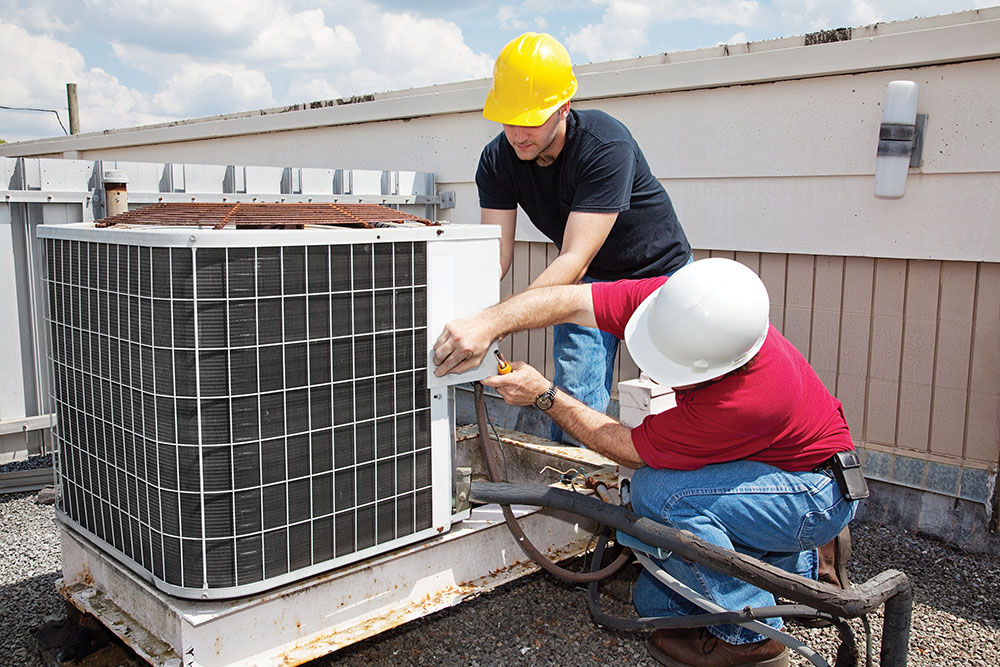
Electrical inspectors are responsible for evaluating the electrical systems, components, and connections within generators to ensure compliance with relevant codes and standards. They meticulously inspect generator installations, wiring, grounding, control panels, and protective devices. Through comprehensive examinations, inspectors identify potential hazards such as faulty wiring, improper grounding, or inadequate protection devices, which could lead to electrical shocks, fires, or equipment failure.
Verifying Compliance with Codes and Standards
Electrical inspectors are well-versed in the applicable codes and standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) and manufacturer guidelines. They assess generators against these regulations to confirm proper installation, sizing, ventilation, fuel storage, and exhaust systems. Inspectors also ensure that the generator is located in a safe and accessible area, away from combustible materials, and protected against environmental elements.
Reviewing Safety Features and Systems
Inspectors thoroughly examine safety features incorporated within generators. This includes inspecting automatic transfer switches (ATS), which facilitate a seamless transition from utility power to generator power during outages, preventing dangerous backfeeding scenarios. Inspectors assess the functionality of ATS devices, ensuring they are properly installed, wired, and interconnected to safeguard against accidents and injuries.
Assessing Grounding and Bonding
Proper grounding and bonding are fundamental to the safe operation of generators. The inspection of grounding systems to verify that they meet the required specifications is critical to the overall safety of the system. Inspectors also ensure that generators are correctly bonded to provide a low-resistance path for fault currents, safeguarding personnel and equipment.
Inspecting Fuel Systems
Fuel systems are critical components of generators, and their safe operation is essential. The review of fuel storage, transfer, and containment systems ensures compliance with applicable codes. As part of this, the fuel tanks, pipes, fittings, and connections must be inspected, looking for signs of leaks or other potential hazards. By ensuring the integrity of the fuel systems, inspectors help prevent fuel-related accidents, fires, or environmental contamination. Additionally, the amount of fuel must be checked to make sure that there is sufficient backup energy where systems are used in critical areas – such as hospitals.
Identifying Maintenance Requirements
Electrical inspectors play a vital role in assessing the overall condition of generators and identifying maintenance needs. They inspect and evaluate the integrity of generator components, including engines, alternators, cooling systems, and control panels. By identifying potential maintenance requirements, inspectors help prevent unexpected breakdowns, improve reliability, and extend the lifespan of the generator.
In short, electrical inspectors serve as guardians of generator safety and reliability. Their thorough inspections, compliance verifications, and meticulous assessments play a crucial role in identifying potential hazards and ensuring that generators meet safety codes and standards. By actively promoting generator safety and reliability, electrical inspectors contribute to the protection of personnel, the ,prevention of accidents, and the uninterrupted functioning of critical systems. Their expertise and commitment help instill confidence in generator operators and end-users, ensuring that these valuable power assets perform optimally when they are needed most.










Find Us on Socials