Summer is here. The kids are home from school, the air conditioning units are firing up, and household appliances such as microwaves are getting used more frequently throughout the day. Between 2014-2018, fire departments in the United States responded to an estimated average of 172,900 home structure fires per year started that started in the kitchen. It’s estimated that kitchen fires account for more than $1 billion in property damage every year, not to mention nearly 5,000 injuries and 550 deaths.
While many kitchen fires are caused by open flames, others are caused by kitchen appliances. The top five kitchen appliances responsible for many fires include ranges and stoves, refrigerators, dishwashers, microwaves, toasters, and ovens. ESFI reported that ranges and stovetops alone cause 62% of home fires. To help prevent many of the fires caused by appliances, from ranges to heating units, it’s our job as installers and inspectors to ensure these systems are installed and functioning properly.
In the 2023 National Electrical Code (NEC), Article 422, Appliances, covers these types of appliances that are either cord-and-plug-connected or fastened in place. Let’s start by examining what exactly the NEC means when it comes to the term “appliance.”
Definitions
The standard definition of the word appliance is normally “individual pieces of equipment for use in the home to perform domestic chores.” These would include a stove, dishwasher, or refrigerator. Article 422 of the NEC expands the scope of these types of electrical equipment to include appliances that are fastened in place or cord-and-plug connected, such as air-conditioning units, water heaters, dishwashers, heating appliances, and infrared heating lamps.
Therefore, the definition in Article 100 has a more expansive view of what exactly an appliance is. It’s defined as “utilization equipment, generally other than industrial, that is fastened in place, stationary, or portable; is normally built in a standardized size or type; and is installed or connected as a unit to perform one or more functions such as clothes washing, air-conditioning, food mixing, deep frying, and so forth.”
Another specific definition that applies to appliances is appliance branch circuits. These are defined as “a branch circuit that supplies energy to one or more outlets that appliances are going to be connected to and that has no permanently connected luminaires that are not part of an appliance.”
Listing & Labeling
Section 90.7 requires that the installer check to ensure that the appliance has a label from a qualified electrical testing laboratory. In addition, if the appliances are supplied by 50 volts or higher, Section 422.6 requires that they are listed.
One can normally find the wattage of most appliances stamped on the bottom or back of the appliance or on its nameplate. The wattage listed is the maximum power drawn by the appliance. Sometimes, the amperes might be stamped on the unit rather than the wattage Most appliances in the United States use 120 volts. Larger appliances, such as clothes dryers and electric cooktops, use 240 volts.
Protection for Appliances
Appliances that are 150 volts or less to ground and 60 amperes or less, single- or three-phase are required to be provided with Class A GFCI protection for personnel per Section 422.5. This requirement applies to the listed appliances, whether they are hard-wired or cord-and-plug-connected. Multiple GFCI devices are allowed but not required. Appliances that require this protection include:
- Automotive vacuum machines
- Drinking water coolers and bottle fill stations
- Cord-and-plug connected high-pressure spray washing machines
- Tire inflation machines
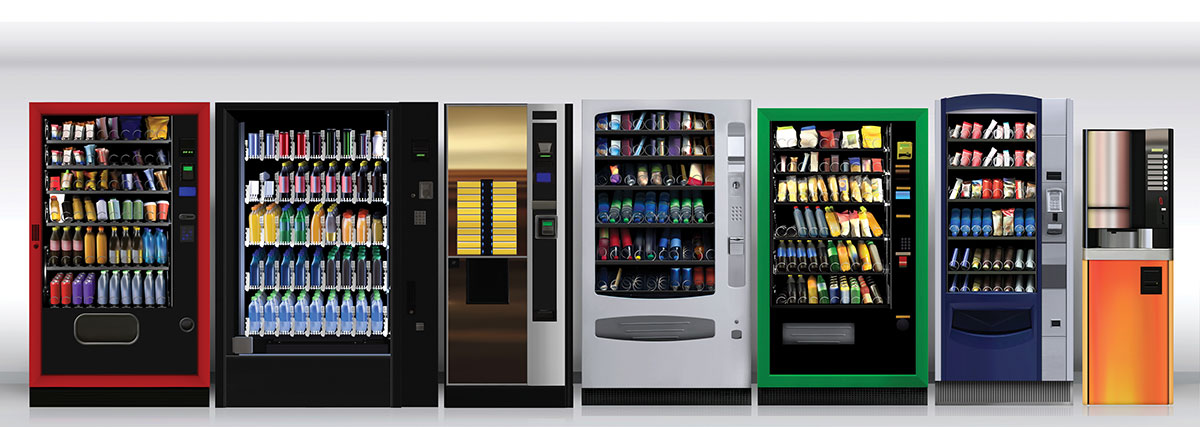
- Vending machines
- Sump pumps, and
These GFCI devices are also required to be readily accessible per subsection (B).
Branch Circuits. Branch circuits that supply appliances are covered in Section 422.10. Individual branch circuits supplying appliances must comply with the requirements in subdivision (A)(1) through (4). The ampacities of the branch-circuit conductors are not allowed to be less than the marked rating for the appliance or the marked rating of an appliance having combined loads. The ampacities for motor-operated appliances that do not have a marked rating are required to be in accordance with Part II of Article 430, Motors, Motor Circuits, and Controllers. For non motor-operated appliances, the branch circuit rating for an appliance that is a continuous load cannot be less than 125 percent of the marked rating or less than 100 percent. The requirements for ranges and cooking appliances are required to be sized in accordance with 210.19(C) and also be allowed to be sized in accordance with Table 220.55.
For branch circuits supplying two or more loads (B), the rating is required to be determined per Section 210.23.
Overcurrent Protection. Section 422.11 requires overcurrent protection for appliances. Subdivision (A) has provisions for appliances with a protective rating on them; the branch-circuit overcurrent device rating is not allowed to exceed the rating on the appliance. This rating does not tell you how much current the appliance will draw but rather the maximum breaker size for the circuit that supplies said appliance.
If there is no breaker marking on the appliance, a maximum may still apply. Several types of appliances have maximums, as denoted in 422.11(B) through (G). If that reference still doesn’t tell you the maximum, search for it online for that specific appliance and/or contact the manufacturer.
Specific Appliances
Central heating equipment is required to be supplied by an individual branch circuit (Unless it is a fixed electric space-hearing appliance) per 422.12. Exception No. 1 allows for auxiliary equipment associated with the heating equipment, such as pumps or valves, to be connected to the same individual branch circuit. The second exception allows a permanently connected air-conditioning unit to be supplied from a branch circuit that supplies central heating equipment other than fixed electric space-heating equipment because central heating equipment and air-conditioning equipment are considered unlikely to operate at the same time.
Storage-Type Water Heaters are covered under 422.13 with a requirement that the branch-circuit overcurrent device and conductors for fixed storage-type water heaters with a capacity of 450 L (120 gallons) or less have an ampere rating of not less than 125 percent of the ampere rating of the water heater. The branch-circuit rating is determined per 422.10.
Flexible Cords. The requirements for flexible cords are covered under 422.16. Subdivision (A) gives permission for these cords to connect appliances to facilitate their frequent interchange or prevent the transmission of voice or vibration and to facilitate the removal or disconnection of appliances that are fastened in place, where the fastening means and mechanical connections are specifically designed to permit ready removal for maintenance or repair. New list item (3) in the 2023 NEC requires that the cord-and-plug-connected electrically heated appliances that produce temperatures over 121°C (250°F) on surfaces in which the flexible cord is likely to be in contact be provided with one of the types of heating cords that are listed in Table 400.4.
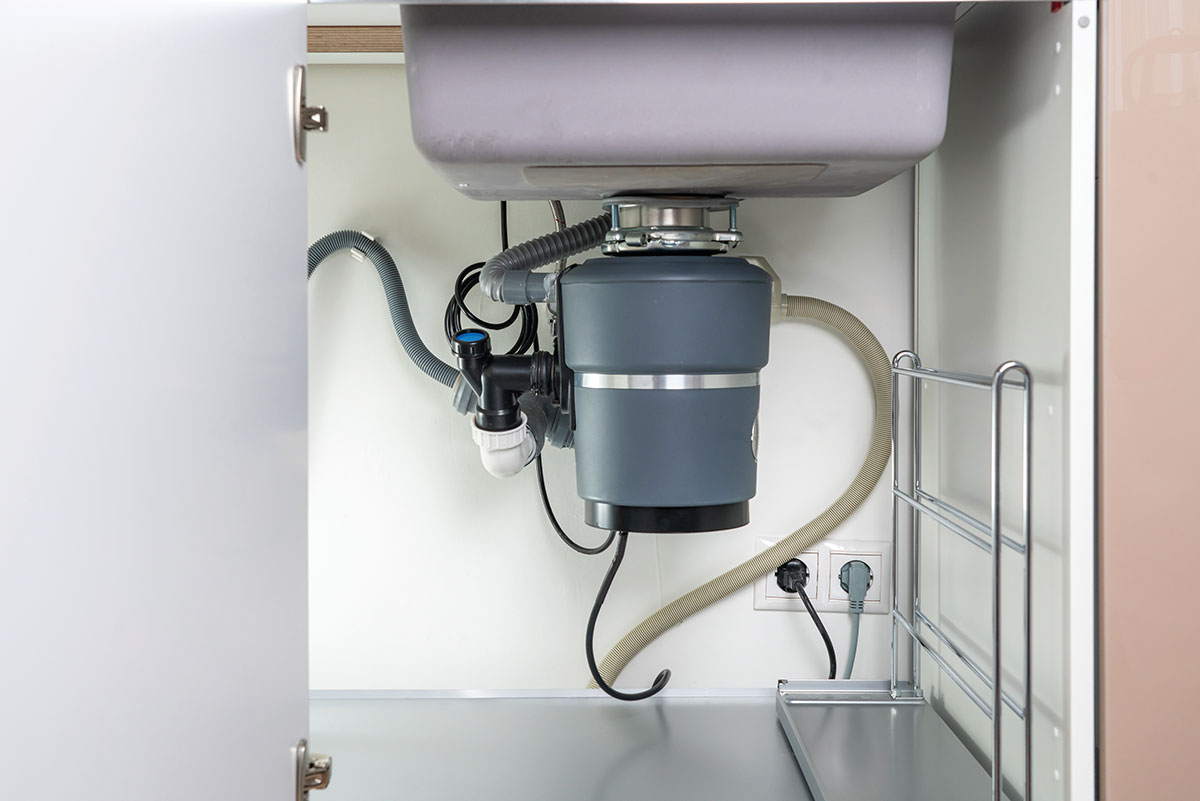
Subdivision (B) covers specific appliances that might use flexible cords. List item (1) covers in-sink waste disposers, whether they are in a sink in a kitchen cabinet, prep area at a deli counter, or under a bar. List item (2), Build-in Dishwasher and Trash Compactors, was updated in the 2023 NEC to add provisions for supply cords to trash compactors and dishwashers to be able to pass through an item like with a wood cabinet to be provided with protections that include a smoothed edge. The flexible cord is now required to be protected against damage by a bushing, grommet, smoothed edge, or other approved means.
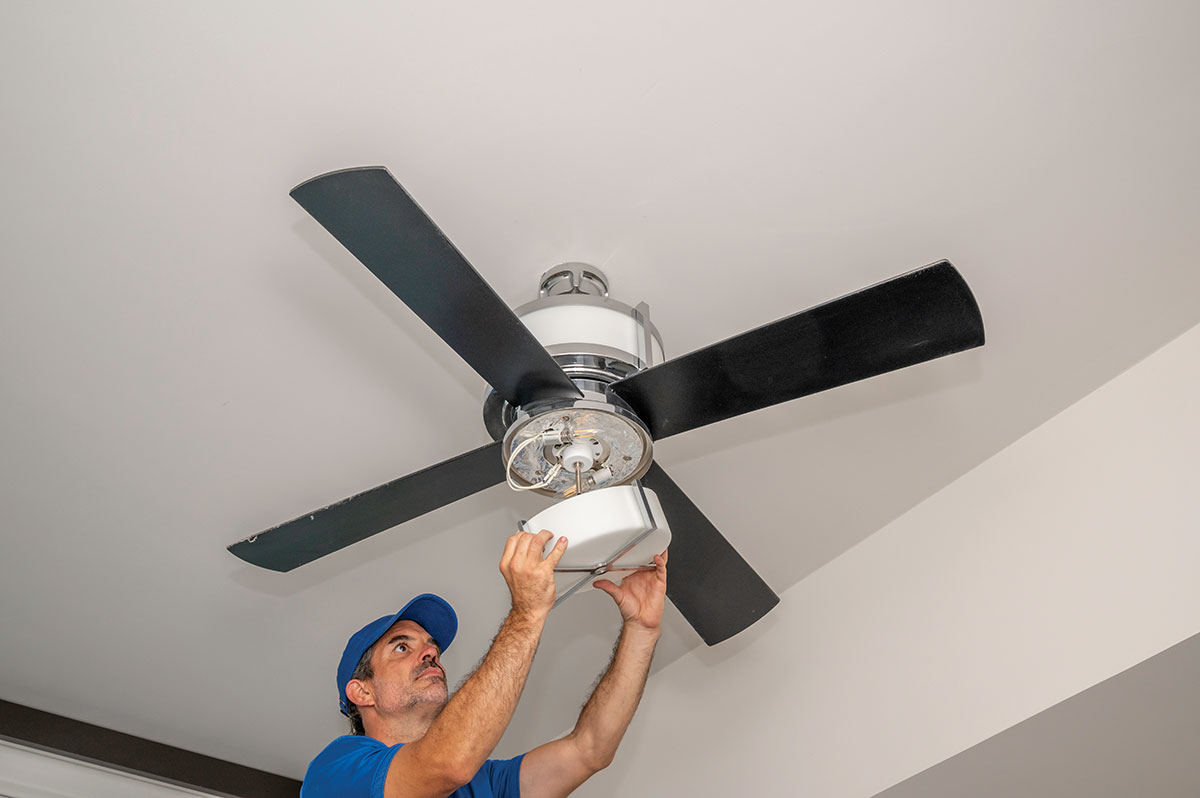
Ceiling-suspended (paddle) fan requirements are covered by Section 422.18 with new subdivision (A) requiring that these fans be supported independently of an outlet box or by a listed outlet box or system identified for fan support installed in accordance with 314.27(C) or a listed outlet box system, weight-supporting ceiling receptacle, and a compatible factory-installed weight-supporting attaching fitting installed per Section 314.27(E). New subdivision (B), Location, prohibits metal parts of ceiling-suspended (paddle) fans in bathroom and shower spaces to be within 900 mm (3 feet) horizontally and 2.5 m (8 feet) vertically from the top of the bathroom rim or shower spaces. This new prohibited zone also correlates with the prohibited zone described in 410.10(D) for luminaires.
Section 422.19, Space for Conductors, further provides the combined volume of the canopy of ceiling-suspended (paddle) fans and outlet box is required to provide sufficient space so that conductors and their connecting devices can be installed per Section 314.16. Outlet boxes are also required to be provided with a cover unless they are covered by means of a ceiling-suspended (paddle fan canopy) per Section 422.20. Section 422.21 requires that any combustible ceiling finish that is exposed between the edge of a ceiling-suspended (paddle) fan canopy or pan and an outlet box that has a surface area of 1160 mm2 (180 in.2) or more must be covered with noncombustible material. Sheetrock ceilings are also not generally considered combustible, so an outlet box under a fan canopy that is recessed into a sheetrock section would not be under the requirements of this section.
The final section covering appliances permitted to use listed weight-supporting ceiling receptacles is Section 422.22, Utilizing Separable Attachment Fittings. This section requires that appliances are permitted to use these listed weight-supporting ceiling receptacles in combination with compatible weight-supporting attachment fittings used within their ratings and in accordance with 317.27(E).
Disconnecting Means
Part III of Article 422 covers disconnecting means. Section 422.30 requires that each appliance must have a means that disconnects simultaneously all ungrounded circuit conductors that it controls.
Appliances Rated at 300 Volt-Amperes or 1/8 Horsepower or Less
For permanently connected appliances that are 300 volt-amperes or 1/8 hp or less, the branch circuit overcurrent device can serve as the disconnecting means where the switch or breaker is within sight of the appliance or is capable of being locked in the open position.
Appliances Rated Over 300 Volt-Amperes
For appliances larger than 300 volt-amperes, Subdivision (B) allows the branch-circuit switch or circuit breaker to serve as the disconnecting means where the switch or circuit breaker is within sight of the appliance or is capable of being locked in the open position in compliance with 110.25.
Motor-Operated Appliances Rated Over 1/8 Horsepower
For these types of appliances, the disconnecting means is required to comply with 430.109 and 430.110, and the disconnecting means must be within sight of the appliance or be locked in the open position per 110.25. The exception for list item (C) permits a switch or circuit breaker serving as the other disconnecting means to be out of sight from the appliance if the appliance is provided with a unit switch that complies with 422.34(A), (B), or (C).
Cord-and-Plug-Connected or Attachment Fitting-Connection Appliances
Section 422.33(A) requires that an accessible separable connector or accessible plug and receptacle combination be permitted to serve as the disconnecting means for these types of appliances. Where these devices are not accessible, cord-and-plug-connected or attachment fitting-and-plug-connected appliances shall be provided with disconnecting means in accordance with 422.31. Subdivision (B) permits attachment plug and receptacle connection at the rear base of ranges for cord-and-plug-connected household electric rangers. The ratings of the receptacle or of a separable connector are not allowed to be any less than any of the connected appliances per subdivision (C).
Unit Switches
Section 422.34 does permit unit switches with a marked-off position that is part of an appliance and subsequently disconnects all ungrounded conductors where other means for disconnection are provided in occupancies as provided in Section 422.34(A) through (D). Section 422.35 does require that the switches and circuit breakers that are used as disconnecting means be of the indicating type. Indicating type just means that they must be marked “On” and “Off” and mounted in the correct orientation.
Construction of Appliances
Part IV covers construction requirements for appliances, which are generally outside of the control of the installer or inspector. However, it does provide some guidance for what to look for when choosing or inspecting specific appliances. Section 422.40 requires that if an appliance is provided with a manually operated, line-connected, single-pole switch for appliance operation, an Edison-base lampholder, or a 15- or 20-ampere receptacle, the attachment plug must be of the polarized or grounding-type.
Cord-and-plug-connected portable, freestanding hydromassage units and hand-held air dryers are required to be constructed to provide protection when immersed per Section 422.41. Types of protectors that comply with this requirement include appliance-leakage circuit interrupters (ALCIs), immersion-detector circuit interrupters (IDCIs), and ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs).
Electrically heated appliances in commercial and industrial locations that are intended to be applied to combustible material are required to be provided with a signal (such as a red light connected to and within sight of the appliance) or integral temperature-limiting device (such as a thermostat) per Section 422.42.
Section 422.44 requires that cord-and-plug-connected immersion heaters be constructed and installed so that current-carrying parts are insulated from electrical contact from the substance in which they are immersed, such as in gas or fluid tanks. Immersion heaters are often used to heat up gases and liquids contained in a tank, vessel, or pipe. Types of immersion heaters can include screw plugs, flanged, and over-the-side. For smoothing irons and other cord-and-plug-connected electrically heated appliances intended to be applied to combustible material, Section 422.45 requires that this equipment be equipped with an approved stand, which is allowed to be a separate piece of equipment or a part of the appliance.
Section 422.47 provides requirements for water heater controls, which are required to be equipped with a temperature-limiting means in addition to its control thermostat to disconnect all ungrounded conductors. The means must be able to sense maximum water temperature and be either a trip-free, manually reset type or a type having a replacement element.
Infrared (heat) radiation lamps are used in industrial locations for a variety of heating and drying purposes. Section 422.48 requires that lamps rated at 300 watts or less are permitted with lampholders of the medium-based, unswitched porcelain type or other types identified for use with infrared heating lamps rated 300 watts or less. For infrared lamps rated over 300 watts, screw shell lampholders are not allowed to be used unless the lampholders are identified as being suitable for use with infrared heating lamps over 300 watts.
Marking
Part V of Article 422 covers marking requirements for appliances. Section 422.60 requires that each electrical appliance is provided with a nameplate giving the identifying name and the rating in volts and amperes or in volts and watts. The marking is also required to be visible or easily accessible after installation. Heating elements rated over one ampere are also required to be legibly marked with the ratings in volts and amperes or in volts and watts or with the manufacturer’s part number per Section 422.61.
The final section in the 2023 edition covers the markings of appliances consisting of motors and other appliance loads is Section 422.62. Subdivision (A) requires that where a motor-operated appliance nameplate includes a horsepower rating, the rating shall not be less than the horsepower rating on the motor nameplate. If there are multiple motors or motors and loads for an appliance, the nameplate value shall not be less than the equivalent horsepower of the combined loads, as calculated with 430.11(C)(1).
Conclusion
Whether installing or inspecting an appliance, it is critical to remain Code-compliant to ensure electrical safety. Peruse the NEC to find other applicable sections that also pertain to appliances. For example, Section 220.53 provides a 75 percent de-rating allowance for four or more appliances that are fastened in place and are supplied by the same feeder or service in a one-family, two-family, or multifamily dwelling. Table 430.248 is also helpful for the full-load current, in amperes, for single-phase ac motors in accordance with 220.50 when dealing with these appliances. Good workmanship and adherence to proper codes and standards can ensure that electrical appliances remain strong and last for years to come.


















Find Us on Socials